Lab 7: Part 2 - More Memory Diagrams
Your task: Writing functions to return specific lists
Create a new file called datingApps.py.
Here is our fictional story for today. There are two new dating apps called fumble and kindling, respectively. Each app uses a list to keep track of their clients. You will write a function for each task below that will return the list shown in the memory diagram. Each diagram builds on prior diagrams so we recommend you start each new function by calling the previous function rather than starting from scratch.
1. makeFumble0
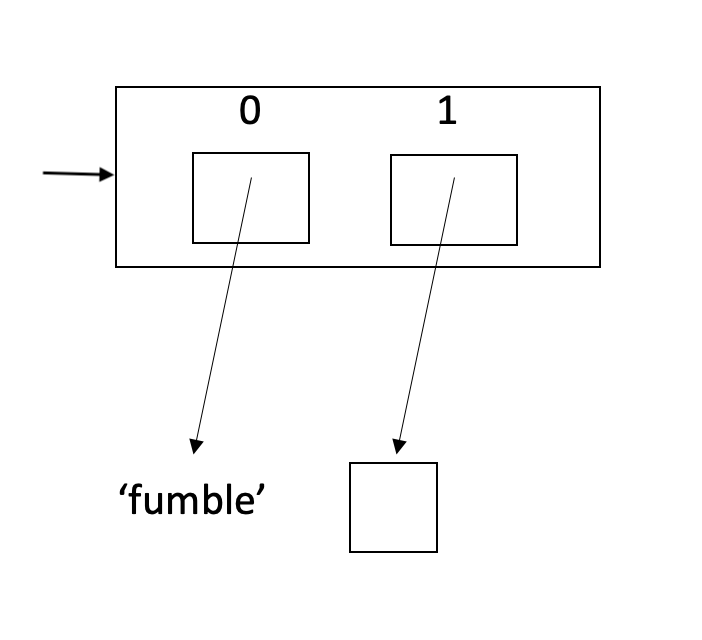
Write a zero-parameter function called makeFumble0 that returns the list shown above. The diagram shows that there are currently no clients signed up on fumble. Note that the empty box represents an empty list.
You can test your function like this:
fumble0 = makeFumble0()
print(fumble0) # should print ['fumble', []]2. makeFumble1
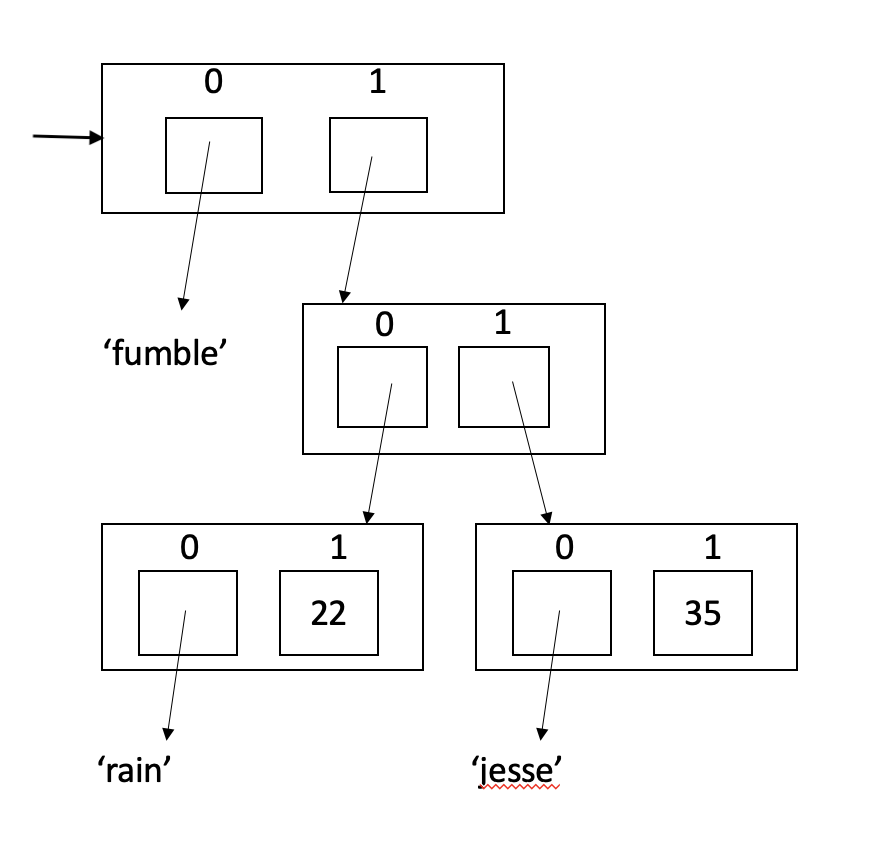
Write a zero-parameter function called makeFumble1 that returns the list shown above. The diagram shows that there are now two clients signed up with fumble: 1) 22 year old Rain and 2) 35 year old Jesse.
You can test your function like this:
fumble1 = makeFumble1()
print(fumble1) # should print ['fumble', [['rain', 22], ['jesse', 35]]]3. makeApps0
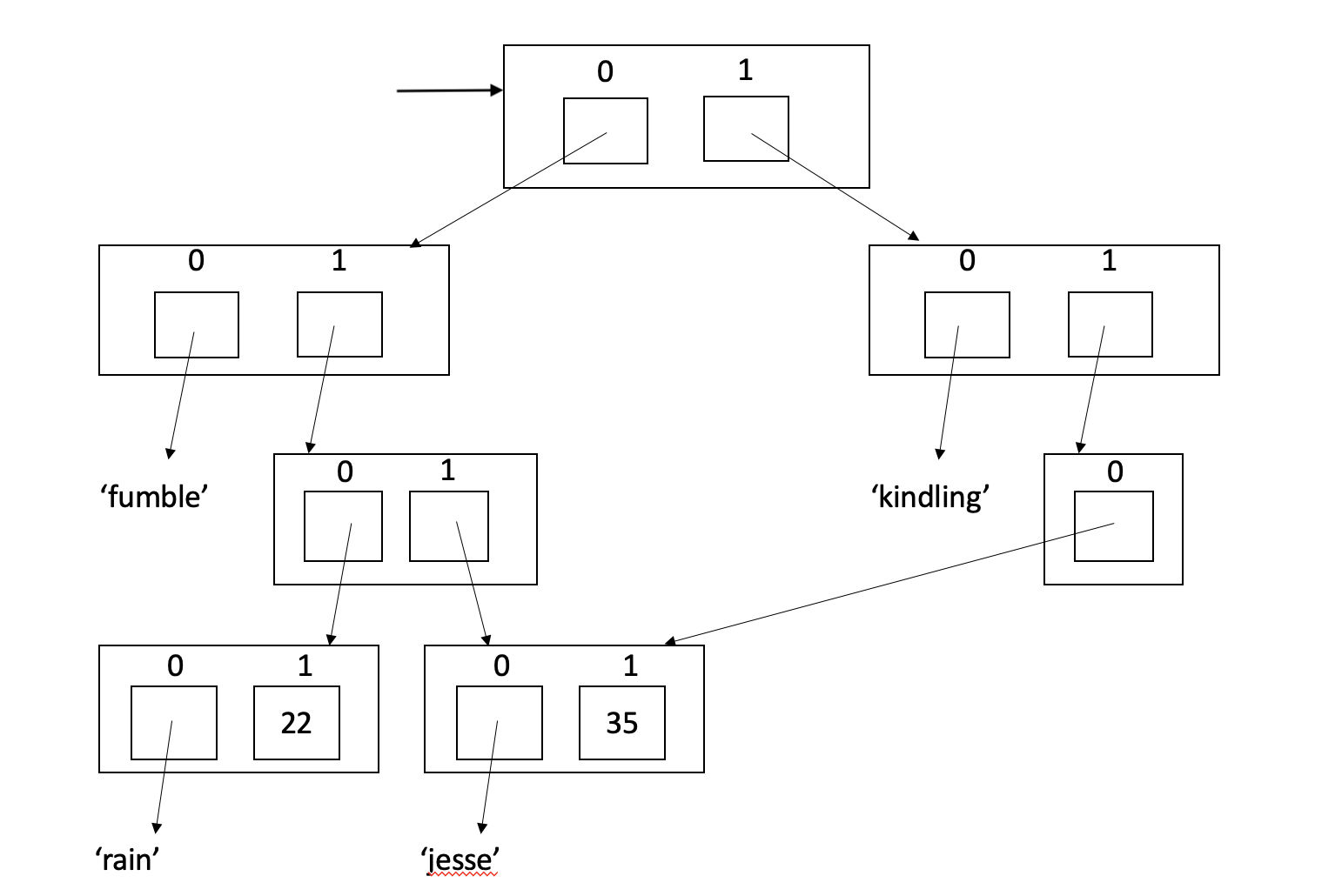
Write a zero-parameter function called makeApps0 that returns the list shown above. The diagram shows that there are two different dating apps. Each app has its own client list.
Jesse, hoping to maximize their chances, signed up with both apps.
You can test your function like this:
both0 = makeApps0()
print(both0)
# [['fumble', [['rain', 22], ['jesse', 35]]], ['kindling', [['jesse', 35]]]]We want to make sure that the two occurrences of Jesse are indeed the same person, so we try this test:
print(both0[0][1][1] is both0[1][1][0]) # Should print True4. makeApps1
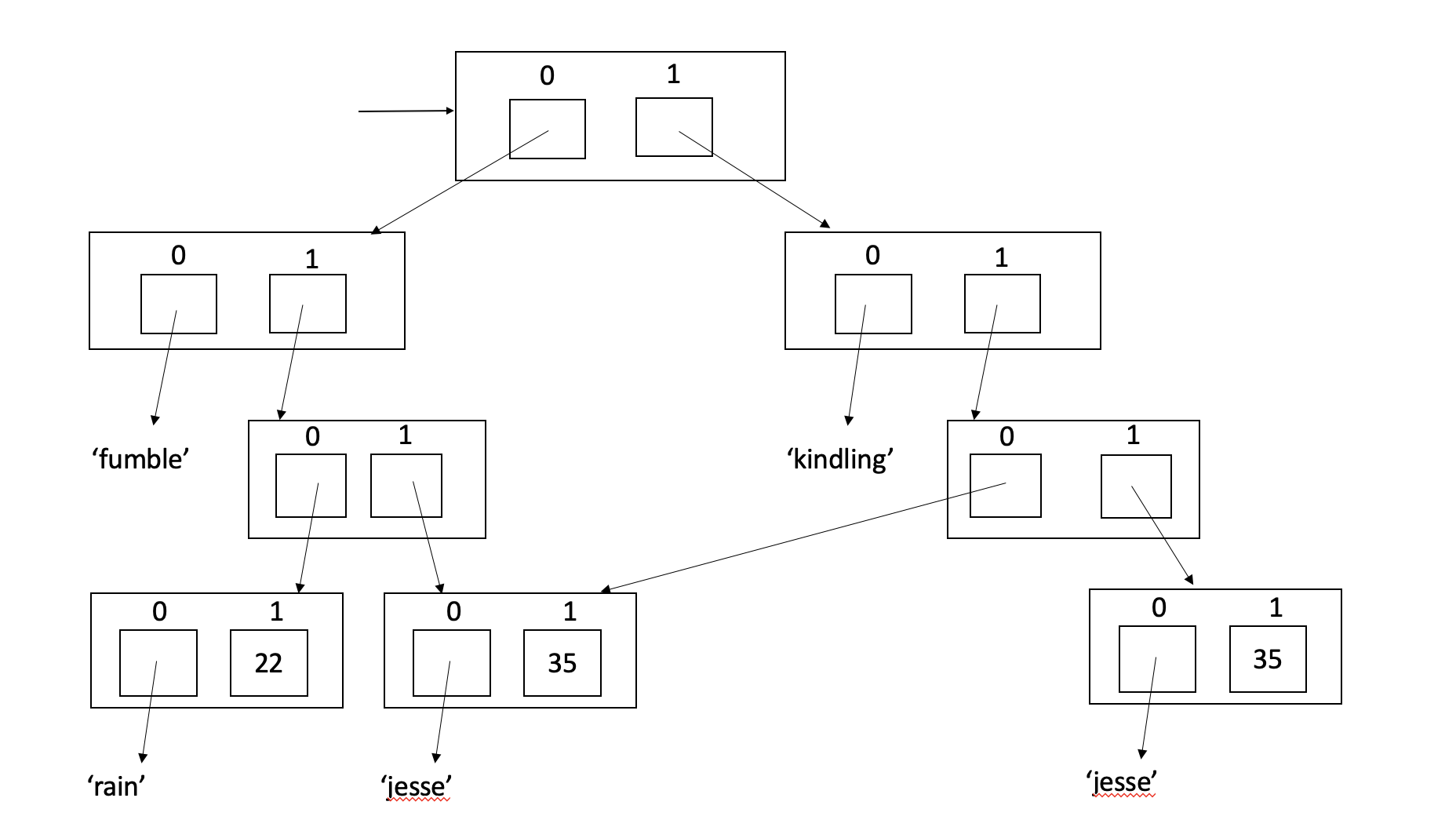
Write a zero-parameter function called makeApps1 that returns the list shown above. The diagram shows that there are two different dating apps. As we saw above,
Jesse, hoping to maximize their chances, signed up with both apps. Turns out there is another human named Jesse, also 35, who also signed up with kindling.
You can test your function like this:
both1 = makeApps1()
print(both1)
# [['fumble', [['rain', 22], ['jesse', 35]]], ['kindling', [['jesse', 35], ['jesse', 35]]]]You can't see aliasing by just looking at the printed list. We want to make sure that the two Jesses in kindling are not the same person, so we try this test:
print(both1[1][1][0] is both1[1][1][1]) # Should print False