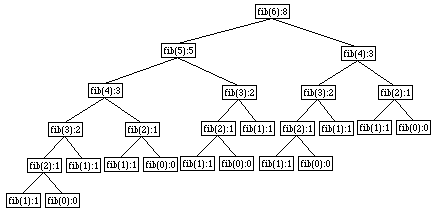
As discussed in class, an invocation tree is an abbreviated version of a Jave Execution Model. It contains a node for each method called during the execution of a program. Each node contains the name of the method, the values of its parameters, and (where applicable) its result. There is an edge connecting each "parent" node to the "children" nodes for the method invocations encountered directly within the body of the parent. The children nodes are all shown at the same vertical level, arranged from left to right in the order of their execution.
For example, consider a recursive definition of the Fibonacci function:
public int fib (int n) {
if (n < 2) {
return n;
} else {
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2);
}
}
Below is an invocation tree for the invocation fib(6). Each node has the form fib(n):r, where n is the parameter of the invocation of fib and r is the result returned by the invocation.

In this problem, you will draw an invocation tree for the invocation of a method that computes an element of Pascal's triangle. Pascal's triangle is a triangular arrangement of numbers whose outer edges consist of 1s and each of whose inner elements is the sum of the two numbers immediately above it to its right and left:
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
1 4 6 4 1
1 5 10 10 5 1
1 6 15 20 15 6 1
Let P(r,i) indicate the value of the i th element in the r th row of Pascal's triangle, where rows are numbered from top to bottom starting with 0, and elements in a row are numbered from left to right starting with 0. For example, P(4,0) = 1, P(4,1) = 4, and P(4,2) = 6.
Here is a recursive method that computes the value of P(r,i):
public int P (int r, int i) {
if ((i == 0) || (i == r)) {
return 1;
} else {
return P(r - 1, i - 1) + P(r - 1, i);
}
}
For this problem, you are to draw a complete invocation tree for the invocation P(6,4). Each node of your tree should have the form P(r,i):a, where r is the row number, i is the element number within a row, and a is the answer returned by the invocation. Be sure to draw your nodes small enough so that they all fit on a single piece of paper. All children of the same parent should appear at the same vertical level, as in the fib example above.
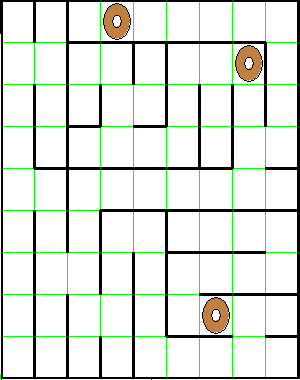
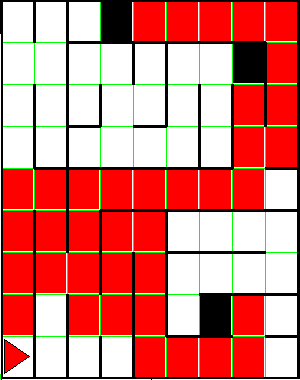
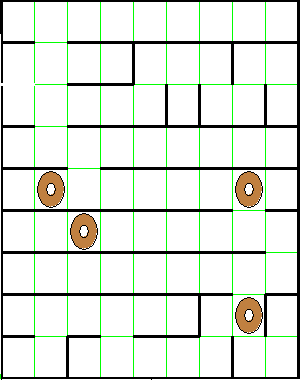
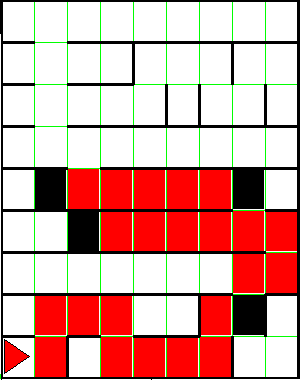
Below are two examples of mazes before and after Harriet has explored them.
Note that Harriet returns to the starting point after exploring the maze.
There will never be a bagel at the starting position.
Think about what strategy you would use to write Harriet's
findBagels method (which is the method which gives
the results below). The findBagels method should return an
integer indicating the number of bagels found. You will want to
define auxiliary methods as well.
Hints: Study the PathFinder example from Friday's lecture. This problem is just a variation of that problem.