|
Lab 6
|

|
Lab 6
|
Download the lab6_programs folder from the
cs111d account on cs.wellesley.edu.
For the following tasks, write your recursive methods and add testing code in the
BagelWorldRec.java file that is provided for you, in lab6_programs.
Note that the tasks today might be challenging for many people. Try as many as you have time during the lab, and don't be disappointed if you don't get to all of them. However, make sure you get back to it, study and understand the solutions once they are posted (some time late on Wednesday.) Tasks 3, 4 and 5 can be worked on in any order. Just choose what is more appealing to you!
System.out.println() statements to the recursive methods
that you will be writing. These statements, when thoughtfully placed, can help
you understand how your program works, and can be a big help in
debugging when your program doesn't work, or doesn't work correctly.
Each time a System.out.println("message");
BuggleWorld.java file:
On the top of the file, there are two lines of code responsible for setting the size of the grid.
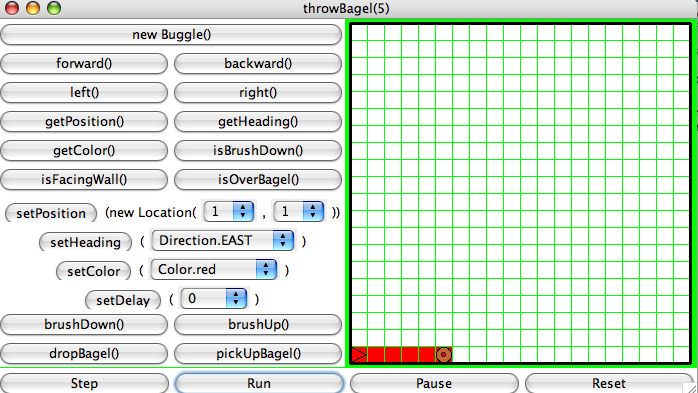
throwBagel(), that places a bagel a number of cells
forward from the buggle's position. The number of cells forward is passed as a parameter to the
method. The position and heading of the buggle should not change after the method has been invoked.
The cells between the buggle's starting position and the bagel's position will be
colored the same color as the buggle's color.
run()
method on an instance of the BagelWorldRec class.
The method run() should look like this:
public void run() {
BagelBuggleRec betty = new BagelBuggleRec();
betty.throwBagel(3);
}
Your
diagram should depict the point in time when the invocation of
run() returns. Although Java can discard an execution
frame when control returns from it, you should not discard any frames
when drawing your diagram.
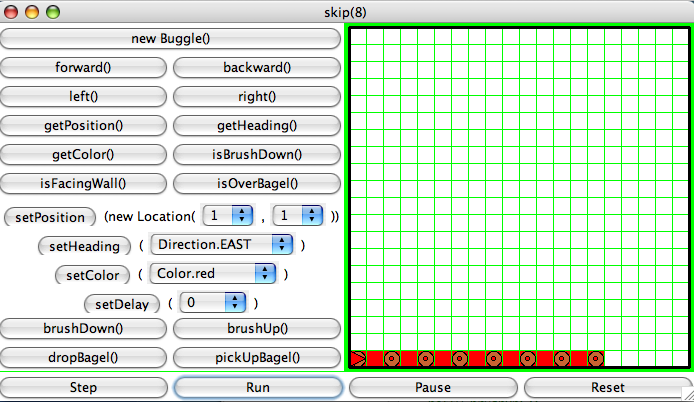
skip(), that produces a row of bagels in every
other cell on a grid. The method takes one integer parameter, n,
that is the number of bagels that are dropped in the row.
The position and heading of the buggle are not changed after the invocation of the method.
Write all your code within the skip() method (no auxiliary methods used),
and do not use the paintCell() method. You can assume there is enough space on
the grid for all the bagels to be placed.
Here is a snapshot of invoking the skip() method:
triangle() that produces a triangle of bagels,
as shown below:
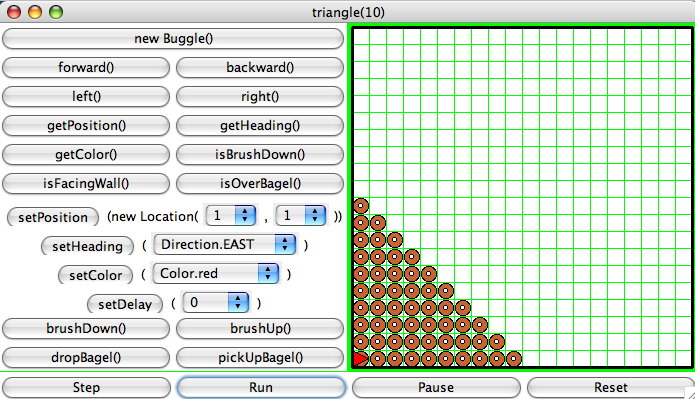
Of course, the size of the basis of the triangle should be flexible.
spiral() that produces a spiral of bagels,
as shown below:
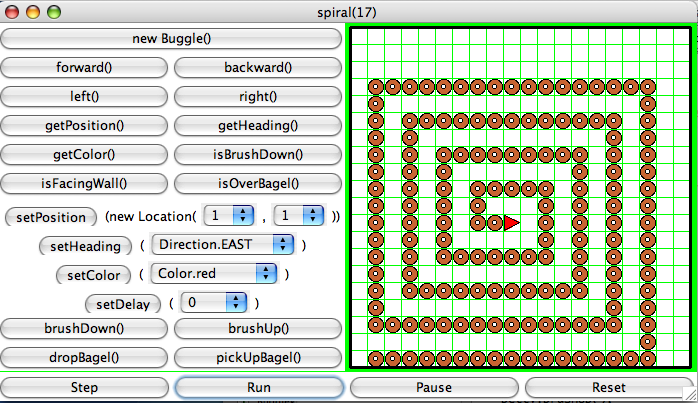
Of course, the size of the outside spiral should be flexible. Notice that you get better-looking spiral in the center when the size of the side of the biggest spiral is a power of 2 + 1 (i.e. size of side of biggest spiral = 2^n +1). Consider this when you are testing your method.