numberItems
numberDone
p
new_p
4
0

4
1


4
2

4
3

4
4

|
L |
index |
total |
|---|---|---|
|
|
1 |
0 |
|
|
2 |
1 |
|
|
3 |
5 |
|
|
4 |
14 |
|
|
5 |
30 |
// while loop implementation
public static int weightedSumWhile(IntList L) {
int index=1; // initialize state variable
int total=0; // initialize state variable
while (!isEmpty(L)) { // continuation is opposite of base case
// be careful, the order state variables are updated does matter!
// update values that depend on other values first!
total = (index*head(L)) + total;
index = index + 1;
L = tail(L);
}
return total;
}
// for loop implementation
public static int weightedSumFor(IntList L) {
int index=1; // initialize state variable
int total=0; // initialize state variable
// pick L as the counter; no initialization necessary
for ( ; !isEmpty(L) ; L=tail(L)) { // update L here
// update state variables; watch the order!
total = (index*head(L)) + total;
index = index + 1;
}
return total;
}
|
L |
sum |
result |
|---|---|---|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
10 |
|
// tail-recursive implementation
public static IntList partialSum(IntList L) {
// call the auxiliary method
// parameters are first row of iteration table
return partialSumTail(L, 0, empty());
}
// auxiliary method
public static IntList partialSumTail(IntList L, int sum, IntList result) {
if (isEmpty(L)) { // base case: stopping condition
return result; // return answer in state variable
} else { // general case: update state variables
sum = sum+head(L); // update sum first since it gets used
// tail-recursive call: generate next row of iteration table
// notice there are no pending operations!
return partialSumTail(tail(L), sum, postpend(result, sum));
}
}
// while loop implementation
public static IntList partialSumWhile(IntList L) {
int sum=0; // initialize state variable
IntList result=empty(); // initialize state variable
while (!isEmpty(L)) { // continuation condition
sum=sum+head(L); // update state variables
result=postpend(result, sum); // paying attention to order
L=tail(L);
}
return result; // return answer after loop is exited
}
|
isMember(3, |
isMember(5, |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
// tail-recursive implementation
public static boolean isMember(int n, IntList L) {
// all state variables are parameters so no auxiliary method needed
// two base cases, must check if list is empty first!
if (isEmpty(L)) { // base case 1: not a member
return false;
} else if (head(L)==n) { // base case 2: is a member
return true;
} else { // general case: tail-recursive call with
return isMember(n, tail(L)); // next row of iteration table
}
}
// for loop implementation
public static boolean isMemberFor(int n, IntList L) {
// pick L as counter; no initialization needed
for ( ; (!isEmpty(L) && (head(L)!=n)) ; L=tail(L));
// semicolon at end of for loop above means there
// are not any statements in the body of the loop
return !isEmpty(L);
}
We've seen how to create "rows" of pictures in PictureWorld. The recursive definition for such a method is given below:
// This method returns a picture with p arranged in numberItems
// equally spaced columns (ie a row with numberItems elements).
public Picture row (Picture p, int numberItems) {
if (numberItems<=0) { // base case: a row with no elements is empty
return empty();
} else { // general case: a row is a picture with a row of one
// fewer number of elements to its right
return beside(p, row(p, numberItems-1), 1.0/numberItems);
}
}
To create an iterative version, we need to eliminate the
pending operation above which is the beside that is
left to do once the recursive call finishes. In order to do that, we
will need to introduce a new state variable which will hold our
partial results at each step of the iteration. For this particular
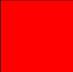
problem, the following state table can be derived for the execution
of
row(patch(Color.red),4)
|
numberItems |
numberDone |
p |
new_p |
|---|---|---|---|
|
4 |
0 |
|
|
|
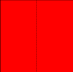
4 |
1 |
|
|
|
4 |
2 |
|
|
|
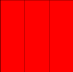
4 |
3 |
|
|
|
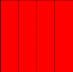
4 |
4 |
|
|
beside(p,new_p,1.0/(numberDone+1))The code for the tail-recursive, while loop, and for loop version
of row are below:
// iterative (tail-recursive) version of row
public Picture rowIter (Picture p, int numberItems) {
return rowTail(numberItems,0,p,empty());
}
public Picture rowTail (int numberItems, int numberDone, Picture p, Picture new_p) {
if (numberDone==numberItems) { // we're finished
return new_p;
} else { // create next row of state table
return rowTail(numberItems, numberDone+1, p,
beside(p,new_p,1.0/(numberDone+1)));
}
}
// while loop version of row
public Picture rowWhile (Picture p, int numberItems) {
Picture new_p = empty(); // initialize state variable
int numberDone = 0; // initialize counter
while (numberDone<numberItems) { // continuation condition
new_p = beside(p,new_p,1.0/(numberDone+1)); // update new_p
numberDone = numberDone + 1; // update counter
}
return new_p; // we're done so return our picture
}
// for loop version of row
public Picture rowFor (Picture p, int numberItems) {
Picture new_p = empty(); // initialize state variable
for (int numberDone=0; numberDone<numberItems; numberDone=numberDone+1) {
new_p = beside(p,new_p,1.0/(numberDone+1));
}
return new_p; // we're done so return our picture
}
Notice the similarity between the while and for loop versions above. A for loop is just syntactic sugar (an easier way of writing) for a while loop. The blue bold lines in the while loop get placed all on one line in the for loop.
polygon(5,75)
|
numSides |
length |
angle |
|---|---|---|
|
5 |
75 |
72.0 |
|
4 |
75 |
72.0 |
|
3 |
75 |
72.0 |
|
2 |
75 |
72.0 |
|
1 |
75 |
72.0 |
|
0 |
75 |
72.0 |
// tail recursive implementation
public void polygon (int sides, int length) {
double angle = 360.0/(double)sides;
polygonTail(sides, length, angle);
}
// auxiliary method
public void polygonTail(int numSides, int length, double angle){
if (numSides > 0) {
fd(length);
lt(angle);
polygonTail(numSides - 1, length, angle);
}
}
// while loop implementation
public void polygonWhile(int sides, int length){
double angle = 360.0/(double)sides;
while (sides > 0) {
fd(length);
lt(angle);
sides = sides - 1;
}
}
// for loop implementation which models the while loop
public void polygonFor(int sides, int length){
double angle = 360.0/(double)sides;
for ( ; sides > 0; sides = sides - 1) {
fd(length);
lt(angle);
}
}
// for loop implementation which uses a counter which counts up
public void polygonFor(int sides, int length){
double angle = 360.0/(double)sides;
for (int s = 1; s <= sides; s=s+1) {
fd(length);
lt(angle);
}
}
flower(6,4,60)
|
numPetals |
length |
sides |
angle |
|---|---|---|---|
|
6 |
4 |
60 |
60.0 |
|
5 |
4 |
60 |
60.0 |
|
4 |
4 |
60 |
60.0 |
|
3 |
4 |
60 |
60.0 |
|
2 |
4 |
60 |
60.0 |
|
1 |
4 |
60 |
60.0 |
|
0 |
4 |
60 |
60.0 |
// tail-recursive implementation
public void flower(int numPetals, int length, int sides) {
double angle = 360.0/(double)numPetals;
flowerTail(numPetals, length, sides, angle);
}
// auxiliary method
public void flowerTail(int numPetals, int length, int sides, double angle){
if (numPetals > 0) {
polygon(sides,length);
lt(angle);
flowerTail(numPetals - 1, length, sides, angle);
}
}
// while loop implementation
public void flowerWhile(int petals, int sides, int length){
double angle = 360.0/(double)sides;
while (petals > 0) {
polygon(sides,length);
lt(angle);
petals = petals - 1;
}
}
// for loop implementation which models the while loop
public void flowerFor(int petals, int sides, int length) {
double angle = 360.0/(double)sides;
for ( ; petals > 0; petals = petals - 1) {
polygon(sides,length);
lt(angle);
}
}
// for loop implementation which uses a counter which counts up
public void flowerFor(int petals, int sides, int length){
double angle = 360.0/(double)sides;
for (int i = 1; i <= petals; i=i+1) {
polygon(sides,length);
lt(angle);
}
}
For this iteration table, we only show the state variables which
change during the course of the iteration.
flowerNestedFor(6,4,60)
|
i |
j |
|---|---|
|
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
2 |
|
1 |
3 |
|
1 |
4 |
|
2 |
1 |
|
2 |
2 |
|
2 |
3 |
|
2 |
4 |
|
3 |
1 |
|
3 |
2 |
|
3 |
3 |
|
3 |
4 |
|
4 |
1 |
|
4 |
2 |
|
4 |
3 |
|
4 |
4 |
|
5 |
1 |
|
5 |
2 |
|
5 |
3 |
|
5 |
4 |
|
6 |
1 |
|
6 |
2 |
|
6 |
3 |
|
6 |
4 |
public void flowerNestedFor(int petals, int sides, int length){
double petalAngle = 360.0/(double)petals;
double polyangle = 360.0/(double)sides;
for (int i = 1; i <= petals; i=i+1) {
for (int j = 1; j <= sides; j=j+1) {
fd(length);
lt(polyangle);
}
lt(petalAngle);
}
}